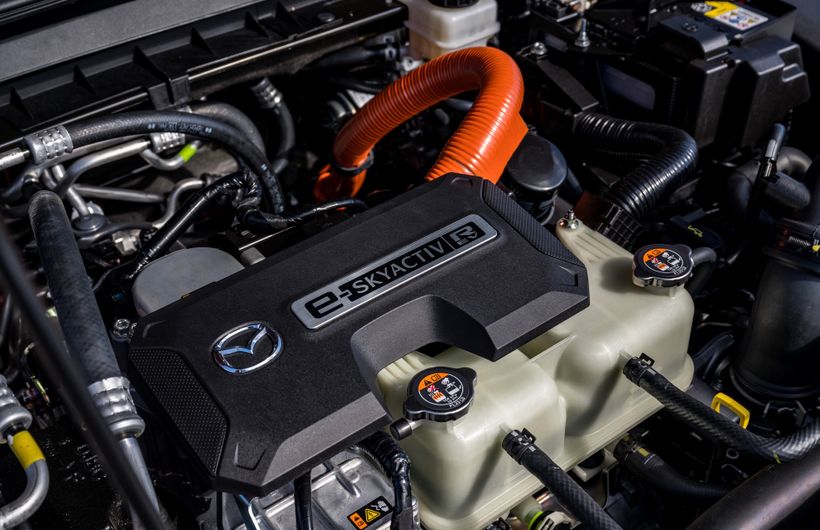
Unless you are a car geek, you might think REX is just the name of next door's dog. But you might soon be looking at one for your next car, as a range extender (REX), or range extended electric vehicle (REEV), is an interesting type of hybrid which is much more electric car than most PHEVs and HEVs. As well as a few models from the likes of BMW and Mazda, they are set to be launched by Volkswagen and several Chinese brands over the next few years.
A REX is battery-powered electric car with an on-board petrol engine that functions as a generator. You'll sometime see this being called an auxiliary power unit (APU), which is engineering speak for a secondary power source. Basically, when a range extender's battery charge is low, the petrol engine starts automatically and charges it up. Unlike self-charging and plug-in hybrids, the range extender doesn’t power the car’s wheels directly, it only charges the battery.
What’s the advantage of a range extender?
In theory, the main advantage of a range extended electric car is that range anxiety should become a thing of the past because the battery will always be topped up by the range extender before it goes flat. As long as you don’t run the fuel tank dry, you won’t get stuck or have to worry about the availability of a public charger.
What are the disadvantages of a range extender?
The main disadvantage is complexity and cost. The range extender petrol engine needs the same sort of care as any conventional piston engine, such as routine services, including oil changes. Range extenders can also suffer more issues with their petrol engines as a result of the engine sitting idle for very long periods (which can actually be quite damaging for a piston engine). Of course, you also still have to visit a filling station forecourt from time to time to put fuel in the tank, and a lot of range extenders have very small fuel tanks and aren't all that economical when the petrol engine is charging the battery, so they can be quite expensive to fuel and may need you to stop frequently on long journeys to fill up with petrol.

Is a range extended vehicle as efficient as a battery-only EV?
Range extenders and the fuel that goes with them add extra weight, which saps energy from the battery when running in pure electric mode. When the engine is turned off (which should be most of the time), it’s like carrying excess baggage around. Basically, a range extender won't be as efficient as a pure electric car.
Which range extenders can I buy today?
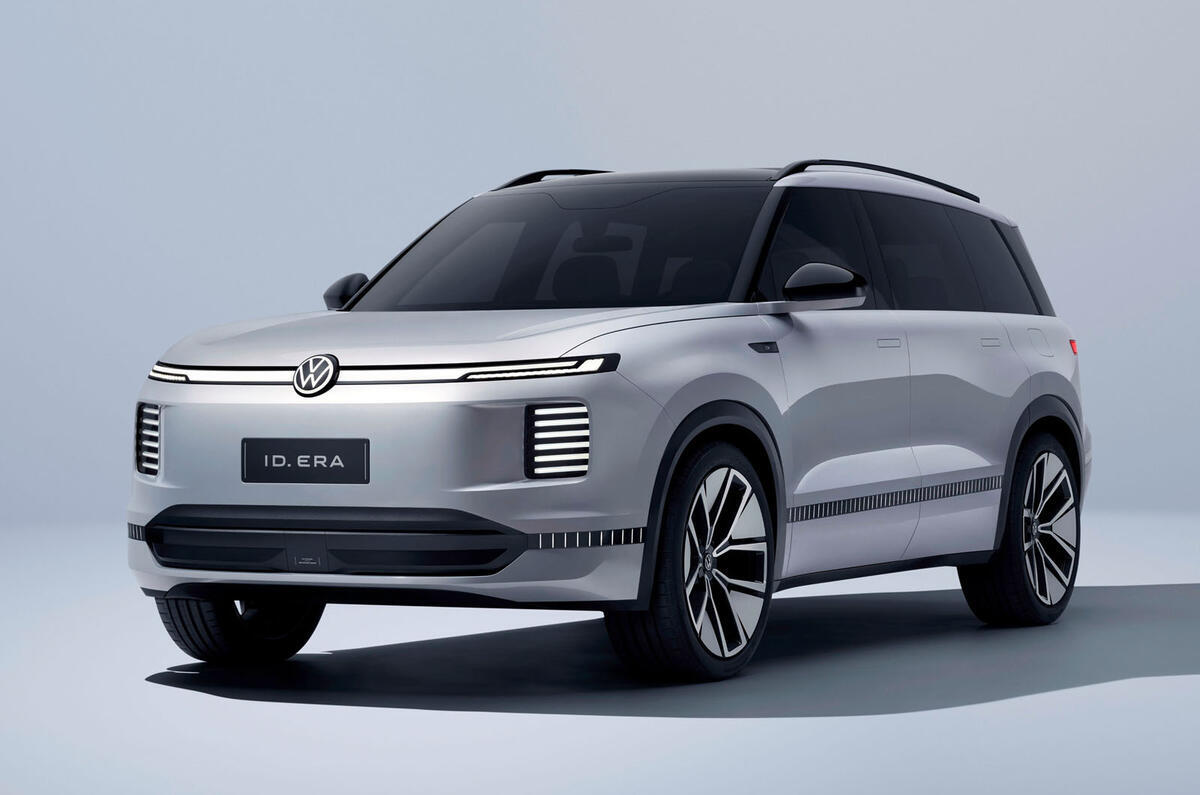
Our favourite is still the BMW i3 Range Extender, which you'll have to buy used as it's not in production any more. Other range extenders are rare, but Mazda still sells the MX-30 R-EV Range Extender. Future models are likely to include a Volkswagen SUV and Chinese brand cars.
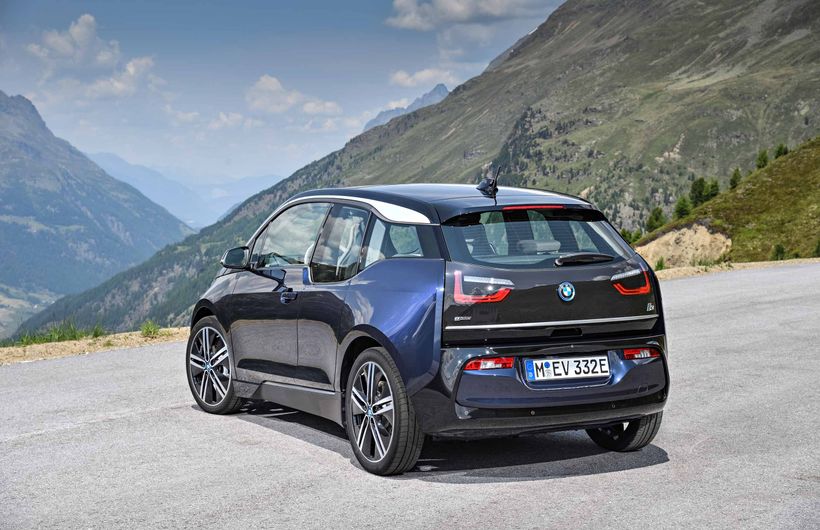 The BMW i3 REX was discontinued when the pure EV's battery range was extended
The BMW i3 REX was discontinued when the pure EV's battery range was extended